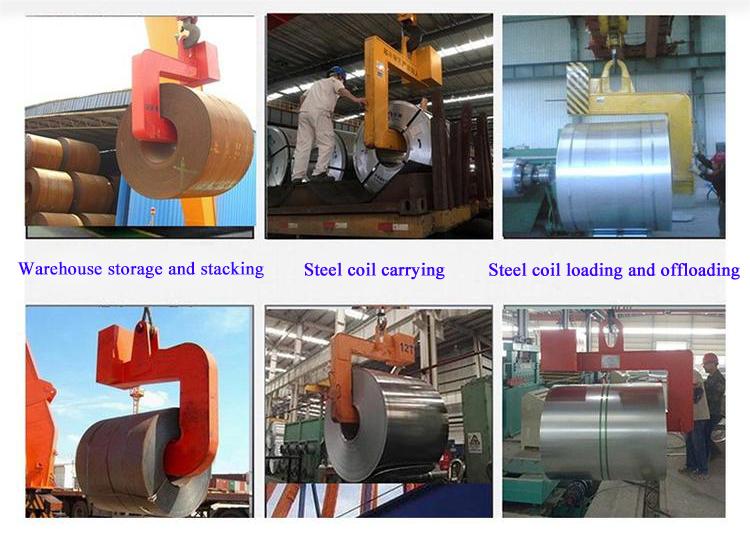
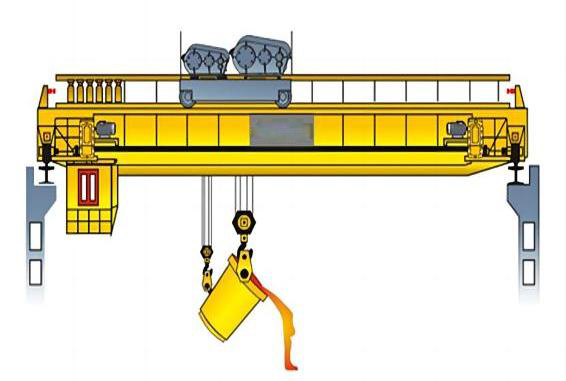
Overview:
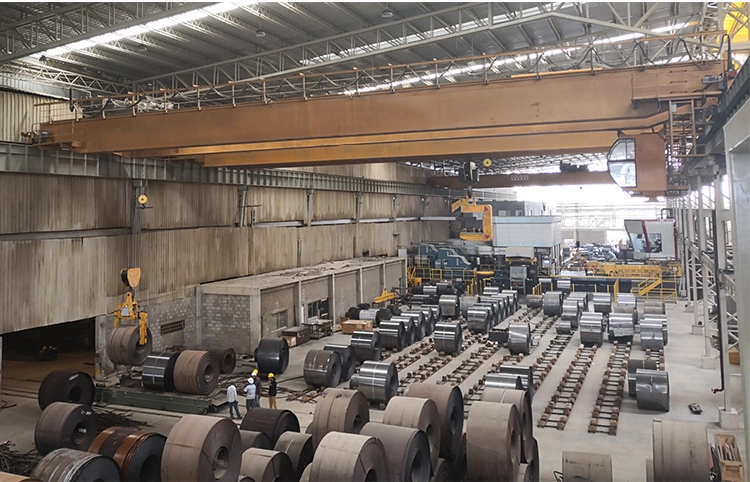

Steel coil cranes are usually used in cold rolling workshops and hot rolling workshops. In continuous operation environments such as steel plants, cranes need to have durability, freedom, and optimal performance in maintenance and quality. Among them, the transmission mechanism is the main and key component of the crane, including motors, gearboxes and brakes.
1. Motor: Cranes use motors as power sources to provide driving force for the crane. The selection of the motor should be reasonably selected based on the workload and operating requirements of the crane to ensure that it can provide sufficient power and torque.
2. Gearbox: The gearbox is an important part of the transmission mechanism, used to transmit the power of the motor and adjust the output speed and torque. It usually consists of multiple gears and shafts, and the force transmission and speed adjustment are achieved through the meshing of the gears.
3. Brake: The brake is used to control the stopping and holding position of the crane. It prevents uncontrolled movement or sliding of the crane when out of service. Brakes usually use friction brakes or electromagnetic brakes to fix the position of the crane by applying braking force.
Features:
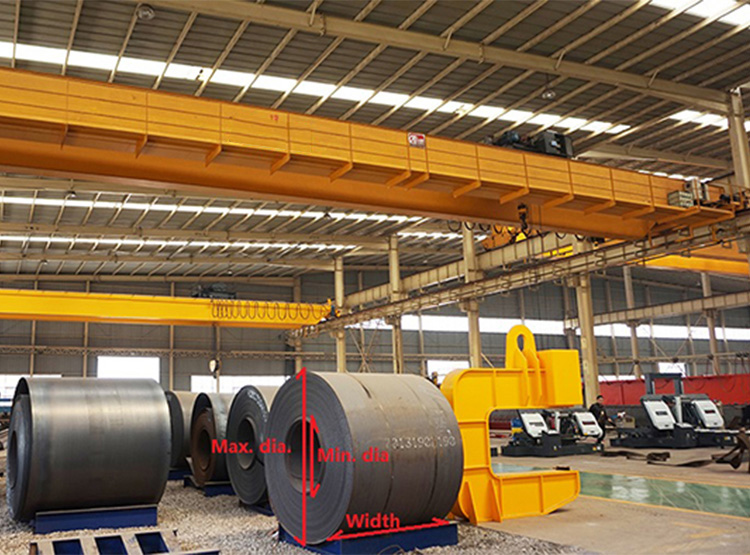

1. Structure: The crane adopts a solid box structure, which is manually welded by a machine to ensure the firmness and stability of the fuselage.
2. Key components: Key components such as wheels, wire rope drums, gears and couplings are manufactured on CNC machining centers to ensure top quality control and precision.
3. Motor: The crane is equipped with a heavy-duty motor, and suppliers include ABB, Siemens, SEW and other well-known brands to provide sufficient power and torque.
4. Electrical system: The crane uses Siemens’ main electrical system to control the operation, manipulation and safety protection of the crane.
5. Surface treatment: The crane undergoes sandblasting surface treatment to improve anti-corrosion performance and enhance the durability of the fuselage.
6. Control methods: The crane is equipped with a variety of control methods, including suspension control, wireless remote control and cab control, etc. to meet different operating needs and improve operational flexibility.
Specification:
Application